
For freelancers and digital agencies, the whirlwind of tasks and deadlines can be daunting. But what if there was a way to bring order to this chaos, streamline your processes, and ensure every project runs smoothly from start to finish? That’s where understanding the project management life cycle comes in.
Managing projects without a clear framework often leads to miscommunication, missed deadlines, and stressed-out teams. You need a structured approach that guides you through each phase, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks. This article is here to help. By diving into the project management life cycle, we’ll show you how to bring clarity and control to your projects. We’ll also introduce you to tools that can make this process even more efficient, such as the SuperOkay client portal, designed to cater specifically to the needs of freelancers and digital agencies.
Ready to transform your project management approach? Let’s dive into the essential stages of the project management life cycle and discover how you can master each one to deliver outstanding results.
What is Project Management Life Cycle and Why is it Important?
Project management is the discipline of planning, executing, and closing projects. It involves coordinating resources, managing teams, and ensuring that project goals are met on time and within budget. At the heart of effective project management lies the project management life cycle, a structured framework that guides you through the entire process from inception to completion.
The project management life cycle is typically divided into five phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Each phase has its own set of tasks and objectives, and together they form a roadmap for managing projects systematically. For digital agencies and freelancers, understanding this life cycle is crucial because it provides a clear path to follow, reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing productivity.
Initiation is where you define the project’s purpose, identify stakeholders, and set initial goals. Planning involves detailed outlining of tasks, timelines, and resources needed. Execution is the phase where the actual work happens, and monitoring and controlling ensure the project stays on track. Finally, closing marks the completion of the project, with evaluations and reflections to learn from the experience.
By adhering to the project management life cycle, you can ensure that all aspects of a project are covered. This structured approach not only improves efficiency but also boosts client satisfaction, as projects are delivered on time and to the expected standards. For freelancers and digital agencies, mastering this life cycle can be the difference between chaotic, stressful projects and streamlined, successful ones.
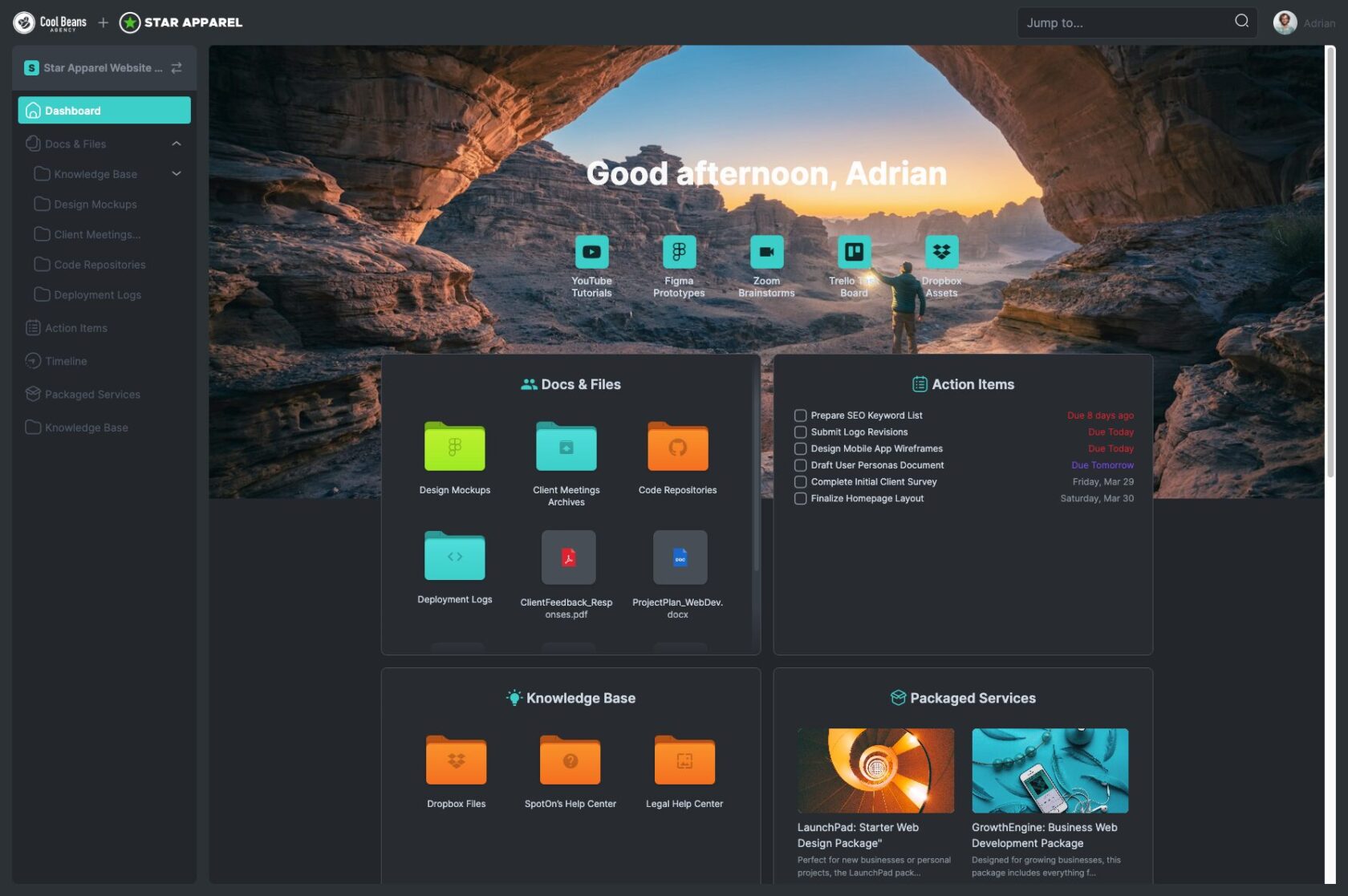
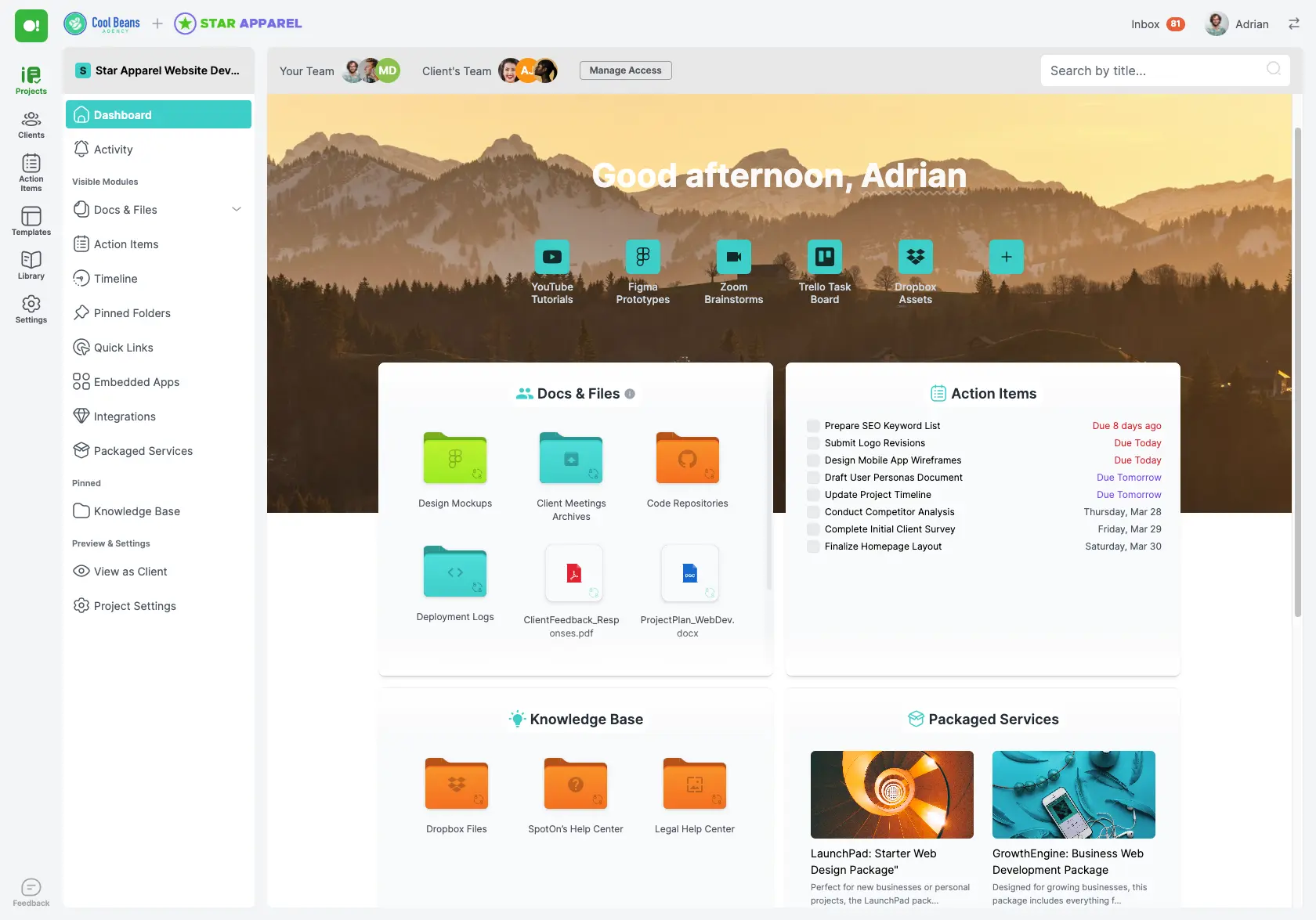
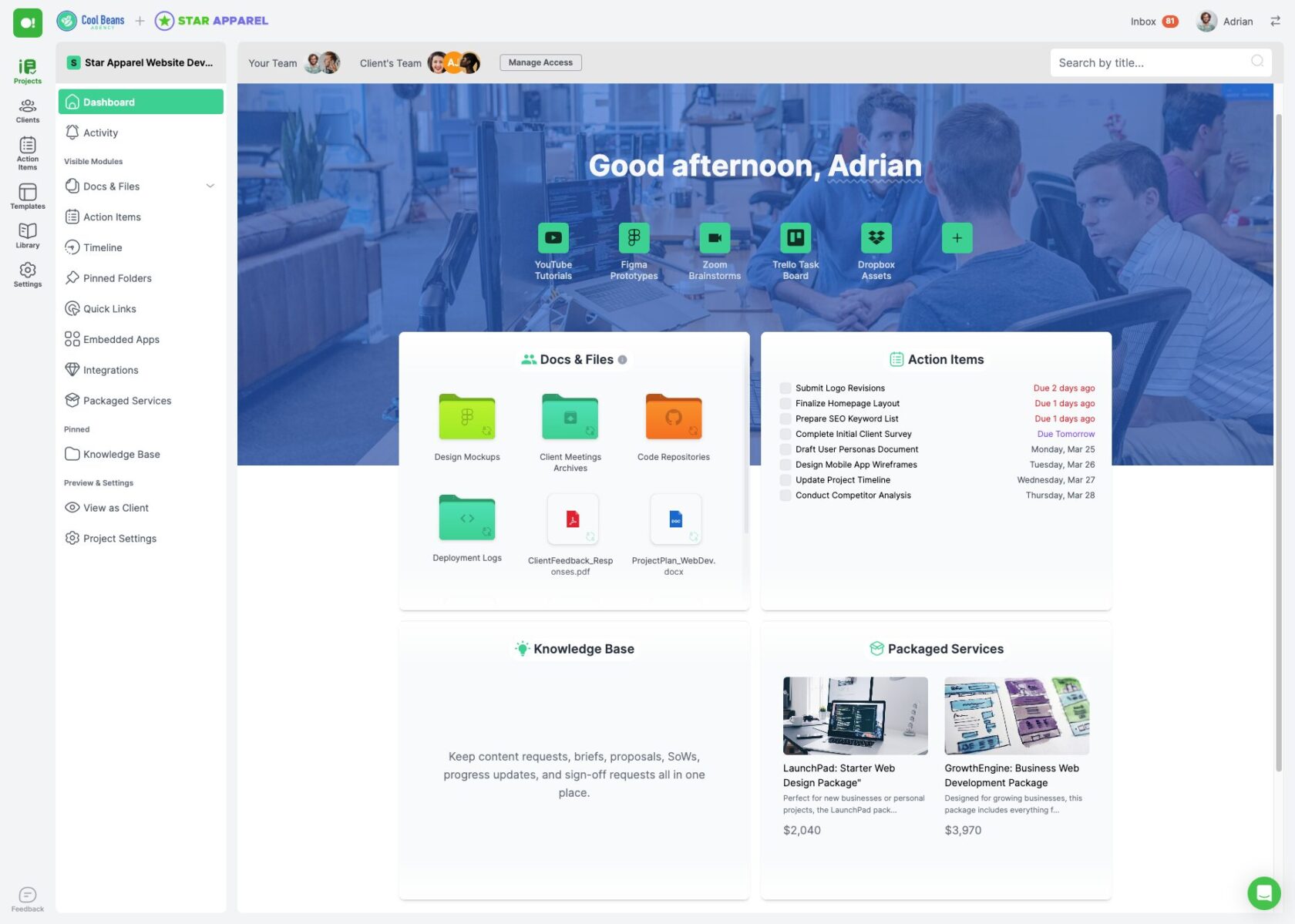
Client Portal
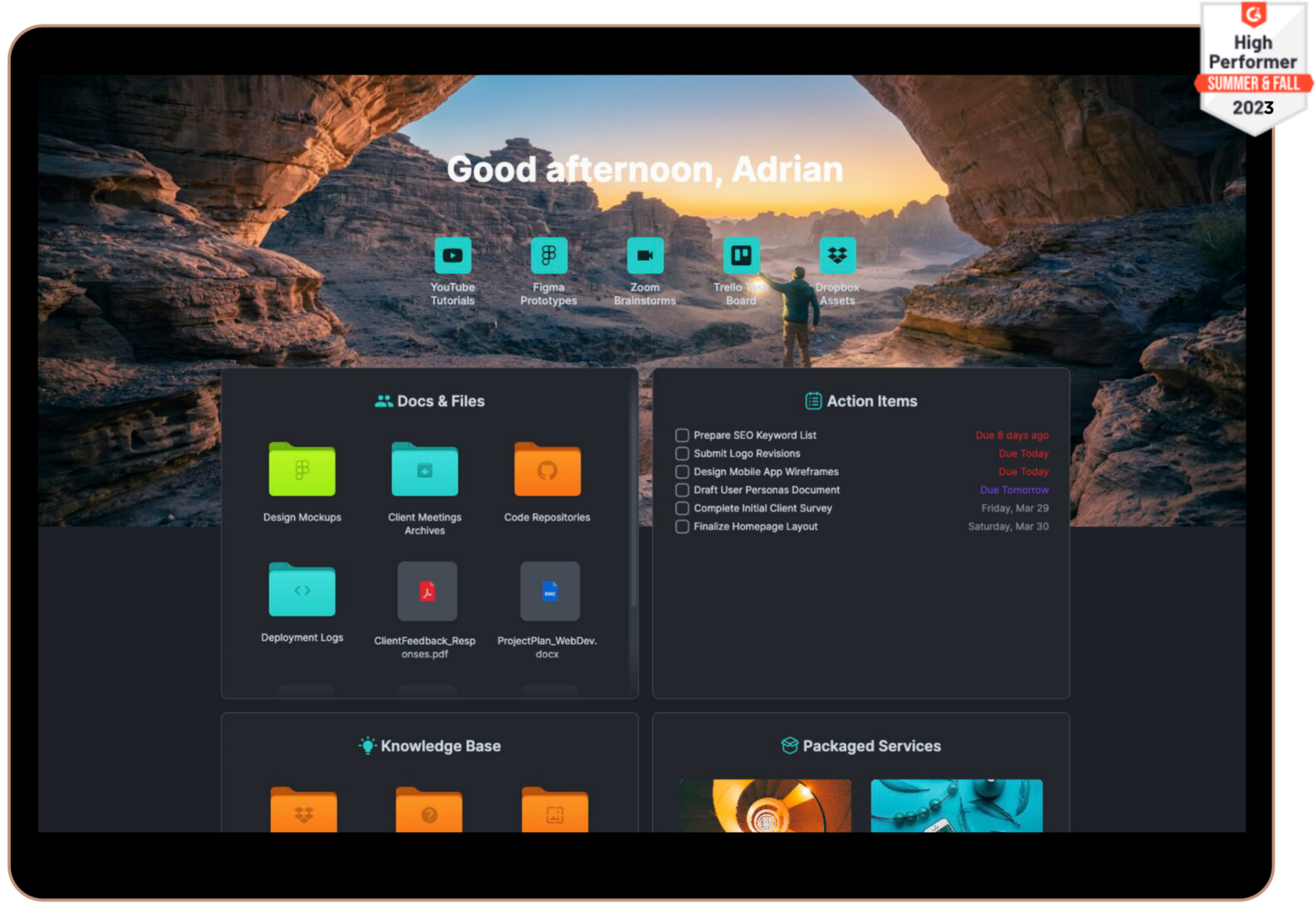
One of the most effective ways to enhance your project management capabilities is by using a client portal. A client portal is a secure, online platform where you can manage all interactions and information related to your projects. For freelancers and digital agencies, a client portal can be a game-changer, bringing organization and efficiency to your workflow.
At SuperOkay, we’ve developed a client portal specifically designed to meet the needs of freelancers and digital agencies. Our platform helps you manage the entire project management life cycle seamlessly, from initiation to closing. Here’s how:
• Centralized Communication: With SuperOkay’s client portal, all communication with your clients is centralized. No more sifting through endless email threads or losing track of important messages. Everything is stored in one place.
• Document Management: Keep all project-related documents organized and easily accessible. Our client portal allows you to upload, share, and collaborate on documents with your clients. This ensures that everyone is on the same page and that important files are always within reach.
• Task and Milestone Tracking: Managing tasks and milestones is a breeze with SuperOkay. Our platform allows you to create and assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress. You and your clients can see at a glance what has been completed and what still needs to be done, ensuring that projects stay on schedule.
• Customizable Templates: Our templates ensure consistency and professionalism in your documents, helping you make a great impression on your clients.
Using a client portal like SuperOkay not only improves your project management but also enhances client satisfaction. By providing a clear, organized, and professional platform for managing projects, you can deliver better results more efficiently. For freelancers and digital agencies looking to elevate their project management game, SuperOkay’s client portal is the perfect tool to make that happen.
🔑 Key Features
• Simple User Interface: Clean, intuitive interface that is easy for clients to navigate
• Fully Customizable: Tailor the look and functionality of the portal to fit your brand and client needs
• Embedded Tools: Features integrations with other tools via “embeds”
• Storage: 1TB with Business Plan
💰 Pricing
Price: Starts at 9$/month (2GB to 1TB, depending on plan)
Free Tier: Yes (500MB)
🧐 Why SuperOkay?
SuperOkay is loved by its users for its exceptional usability and comprehensive feature set, making it a great choice for agencies looking for an easy to use yet powerful client portal.
What sets SuperOkay apart is its ability to combine ease of use with great functionality, making it a simple client portal that does not compromise on features.
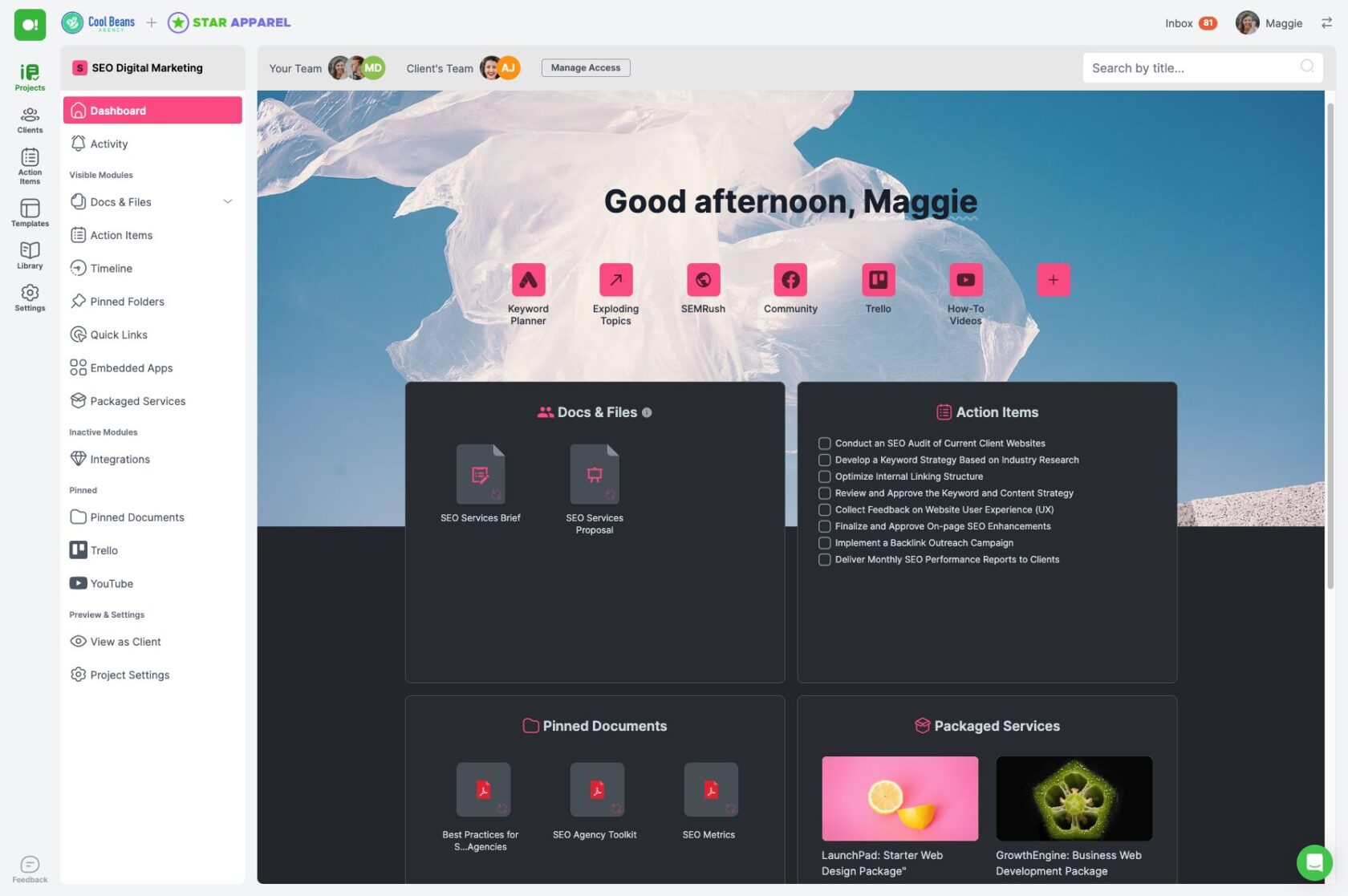
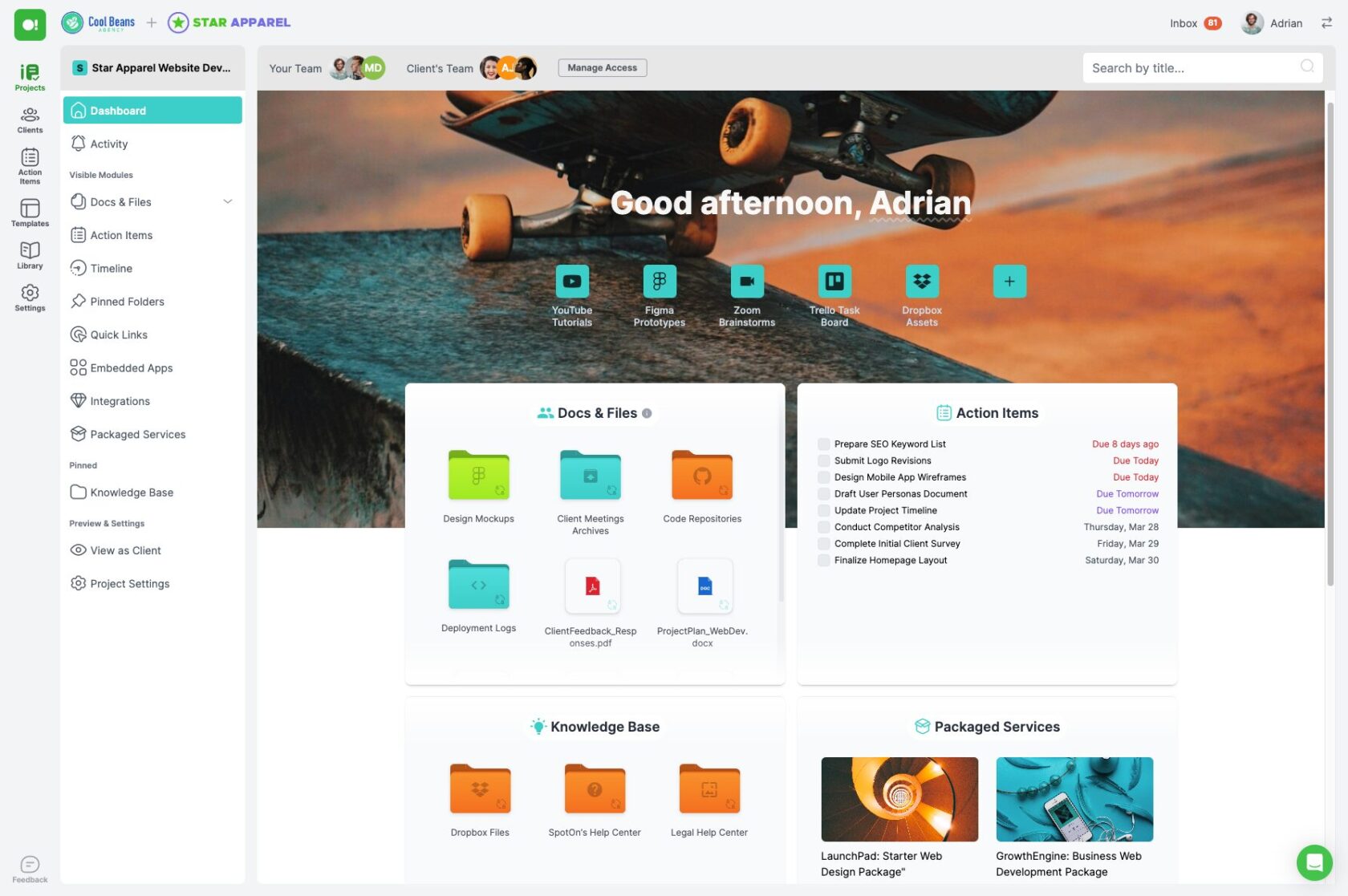
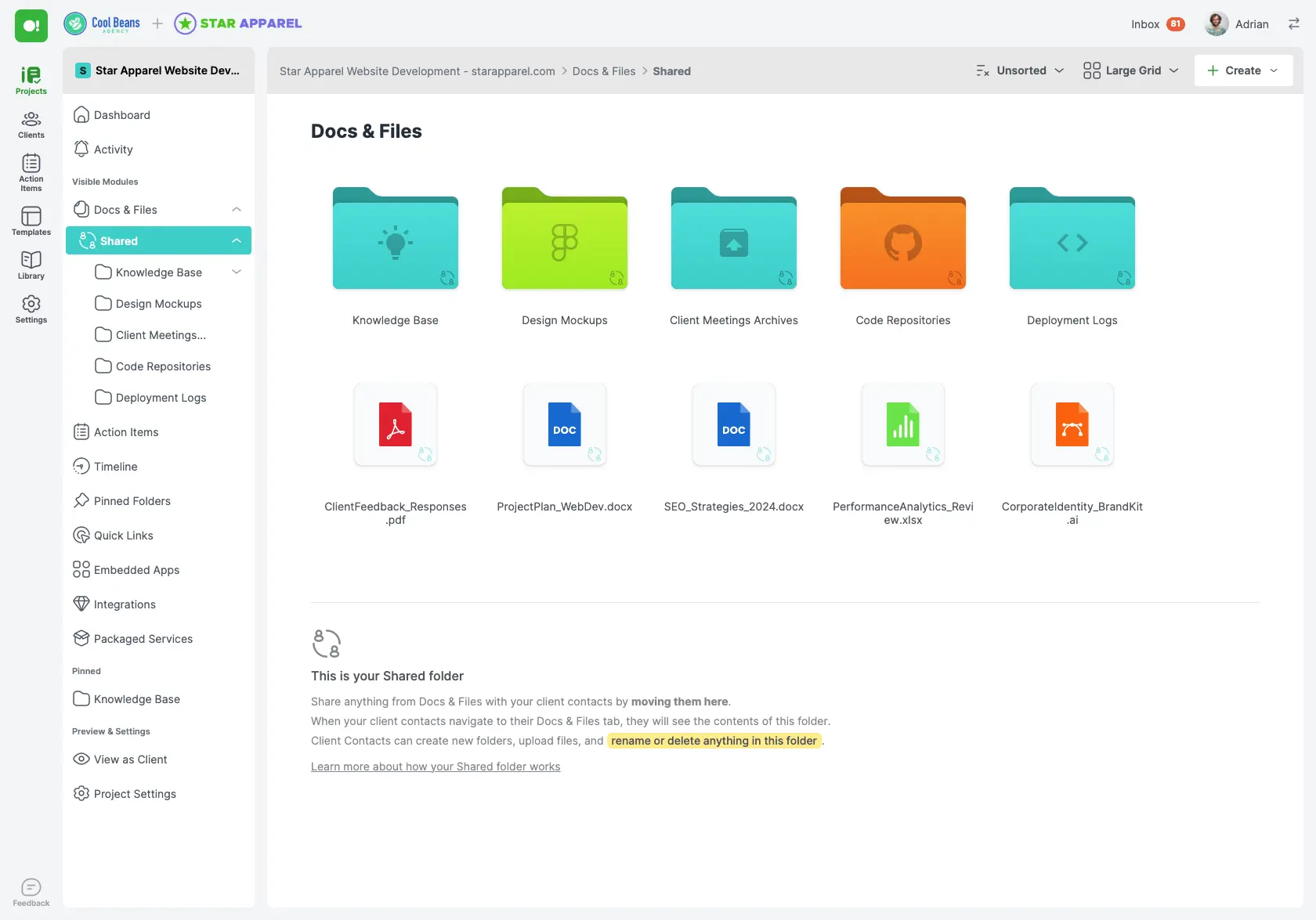
Phase 1: Initiation
The initiation phase is the first and arguably the most critical stage of the project management life cycle. This phase sets the foundation for the entire project, as it involves defining the project’s purpose, identifying key stakeholders, and establishing initial goals and objectives. As a freelancer or digital agency, getting this phase right is essential for ensuring that the project starts on the right foot.
During the initiation phase, you’ll engage in discussions with your client to understand their vision and what they hope to achieve with the project. This involves asking probing questions to uncover their needs, challenges, and expectations. You’ll also need to identify all stakeholders involved, which can include anyone who has an interest in the project’s outcome, such as clients, team members, and end-users.
One of the main deliverables of this phase is the project charter. The project charter is a document that formally authorizes the project and outlines its scope, objectives, and participants. It serves as a reference point for all stakeholders and provides a clear understanding of what the project aims to achieve.
Another critical activity in the initiation phase is conducting a feasibility study. This involves analyzing the project’s viability in terms of time, cost, resources, and technical requirements. The goal is to determine whether the project is feasible and worth pursuing.
By thoroughly completing the initiation phase, you set a clear direction for the project and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned with the project’s goals and expectations. This reduces the risk of misunderstandings and sets the stage for a successful project.
Phase 2: Planning
Once the initiation phase is complete, the project moves into the planning phase. This stage involves developing a detailed roadmap that outlines how the project will be executed, monitored, and controlled. For freelancers and digital agencies, meticulous planning is crucial for managing resources, timelines, and client expectations effectively.
The planning phase begins with defining the project scope in greater detail. This includes specifying the deliverables, tasks, and activities required to complete the project. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is often used to break down the project into manageable sections, making it easier to assign tasks and track progress.
Next, you’ll develop a project schedule. This involves estimating the time required for each task, sequencing the tasks in the correct order, and identifying dependencies. Tools like Gantt charts or project management software can be extremely helpful in visualizing the schedule and ensuring that all team members are aware of their responsibilities.
Resource planning is another critical component of this phase. You’ll need to identify the resources required for each task, which can include personnel, equipment, and materials. Allocating resources efficiently helps ensure that the project stays on track and within budget.
Risk management is also a vital part of the planning phase. This involves identifying potential risks that could impact the project and developing strategies to mitigate them. By anticipating challenges and preparing contingency plans, you can minimize disruptions and keep the project moving forward.
Communication planning is equally important. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols ensures that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project. This includes setting up regular meetings, status reports, and feedback mechanisms.
By the end of the planning phase, you should have a comprehensive project management plan that serves as a blueprint for the execution phase. This plan provides a clear roadmap for achieving the project’s objectives and sets the stage for successful project delivery.
Phase 3: Execution
The execution phase is where the rubber meets the road. In this stage, the project plan is put into action, and the work required to achieve the project’s objectives is carried out. For freelancers and digital agencies, the execution phase is where the bulk of the effort and resources are expended.
During the execution phase, team members complete their assigned tasks and produce the project deliverables. Effective team management is crucial in this phase to ensure that everyone stays focused, motivated, and productive. Regular check-ins and progress meetings can help keep the team on track and address any issues that arise promptly.
One of the key activities in the execution phase is project coordination. This involves managing resources, timelines, and quality to ensure that the project stays on schedule and meets the required standards. Project managers play a pivotal role in coordinating efforts, resolving conflicts, and making decisions that keep the project moving forward.
Communication continues to be a critical factor in this phase. Keeping all stakeholders informed about the project’s progress, changes, and any issues that arise is essential for maintaining transparency and trust. Regular status updates, progress reports, and stakeholder meetings are effective ways to ensure everyone is aligned and informed.
Quality management is another important aspect of the execution phase. This involves monitoring the work being done to ensure it meets the project’s quality standards and requirements. Quality assurance processes, such as reviews, inspections, and testing, help identify and rectify any issues before they become significant problems.
By successfully managing the execution phase, you can ensure that the project deliverables are produced to the required standards and within the agreed-upon timelines and budget. This sets the stage for the final phases of the project management life cycle, where the project is monitored, controlled, and ultimately brought to a successful close.

Phase 4: Closing
The closing phase is the final stage of the project management life cycle. This phase involves wrapping up the project, ensuring that all tasks are completed, and that the project deliverables meet the required standards. For freelancers and digital agencies, the closing phase is essential for formally completing the project and reflecting on the lessons learned.
During the closing phase, you’ll conduct a thorough review of the project to ensure that all objectives have been met. This includes verifying that all deliverables are complete and meet the client’s requirements. Any outstanding issues should be resolved, and the project documentation should be finalized and archived.
A critical activity in this phase is obtaining client approval and sign-off. This formalizes the completion of the project and confirms that the client is satisfied with the work delivered. It’s also an opportunity to gather feedback from the client, which can provide valuable insights for future projects.
Another important aspect of the closing phase is conducting a post-project evaluation. This involves reviewing the project’s performance, identifying successes and areas for improvement, and documenting lessons learned. This reflection helps improve processes and practices for future projects, ensuring continuous improvement.
Finally, celebrate the successful completion of the project with your team. Acknowledging the hard work and achievements of everyone involved boosts morale and fosters a positive working environment.
By effectively managing the closing phase, you can ensure a smooth transition out of the project, leaving your client satisfied and your team ready for the next challenge.
Summary of Stages
| Stage | Description | Key Activities |
| Initiation | Define the project’s purpose, identify stakeholders, set initial goals | Create project charter, conduct feasibility study |
| Planning | Develop a detailed roadmap for project execution | Define project scope, create project schedule, resource planning, risk management, communication planning |
| Execution | Put the project plan into action, complete tasks and produce deliverables | Team management, project coordination, regular communication, quality management |
| Closing | Wrap up the project, ensure all tasks are completed, review performance | Verify deliverables, obtain client approval, conduct post-project evaluation, celebrate success |
Conclusion
We’ve taken you through the project management life cycle, highlighting the key phases that guide a project from inception to completion. From the crucial initiation phase, where you set the foundation, to the detailed planning phase that maps out the project’s path, the execution phase where the real work happens, and finally the closing phase that wraps everything up neatly. By mastering each of these stages, you can ensure that your projects are well-organized, efficient, and successful. Utilizing tools like SuperOkay’s client portal can further enhance your project management capabilities, bringing clarity and efficiency to your workflow. With these insights and tools, you’re well-equipped to tackle any project with confidence and precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the project management life cycle?
The project management life cycle is a structured framework that guides a project from its inception to completion. It is typically divided into five phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closing.
Why is the project management life cycle important?
The project management life cycle is important because it provides a clear roadmap for managing projects. It ensures that all aspects of a project are covered systematically, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing efficiency and client satisfaction.
How can a client portal help in the project management life cycle?
A client portal, like the one offered by SuperOkay, helps centralize communication, manage documents, track tasks and milestones, and provide real-time updates. This enhances organization, transparency, and collaboration throughout the project management life cycle.
What are the key activities in the initiation phase of the project management life cycle?
In the initiation phase, key activities include defining the project’s purpose, identifying stakeholders, setting initial goals, creating a project charter, and conducting a feasibility study.
How do you ensure the successful completion of the closing phase in the project management life cycle?
To ensure successful completion of the closing phase, verify that all deliverables meet the required standards, obtain client approval and sign-off, conduct a post-project evaluation, document lessons learned, and celebrate the project’s success with your team.
Are you already using a Client Portal? SuperOkay gives you 1 client portal free forever to start creating professional-looking Client Portals, custom branded to your clients’ brands – Start today by clicking here!

The 5 Key Project Management Principles and How to Use Them
Project management principles are the guiding foundations that ensure successful outcomes in any project. Understanding the definition and significance of project mana…

4 Reasons To Use Project Management Software with Client Portal
Collaboration plays a crucial role in successful project management. Effective teamwork, communication, and coordination among team members and stakeholders are essent…

Organize Your Life With Client Portal Software
When it comes to managing personal and professional information, the challenges can be overwhelming. However, there’s a powerful solution available: client porta…

What is Graphic Design? (2024 Guide for Beginners)
What is Graphic Design and what is it for? Graphic design is a professional craft where designers create visual content to communicate messages effectively. By utilizi…